Sommaire
Introduction
Le monde est de plus en plus interconnecté, et les lois régissant la protection des droits de propriété intellectuelle évoluent pour suivre le rythme. Les lois sur la propriété intellectuelle visent à garantir que les créateurs de ces œuvres soient dûment reconnus et rémunérés pour leurs efforts. Les lois internationales sur la propriété intellectuelle visent à protéger les droits des créateurs et des inventeurs du monde entier.
Les principaux traités internationaux
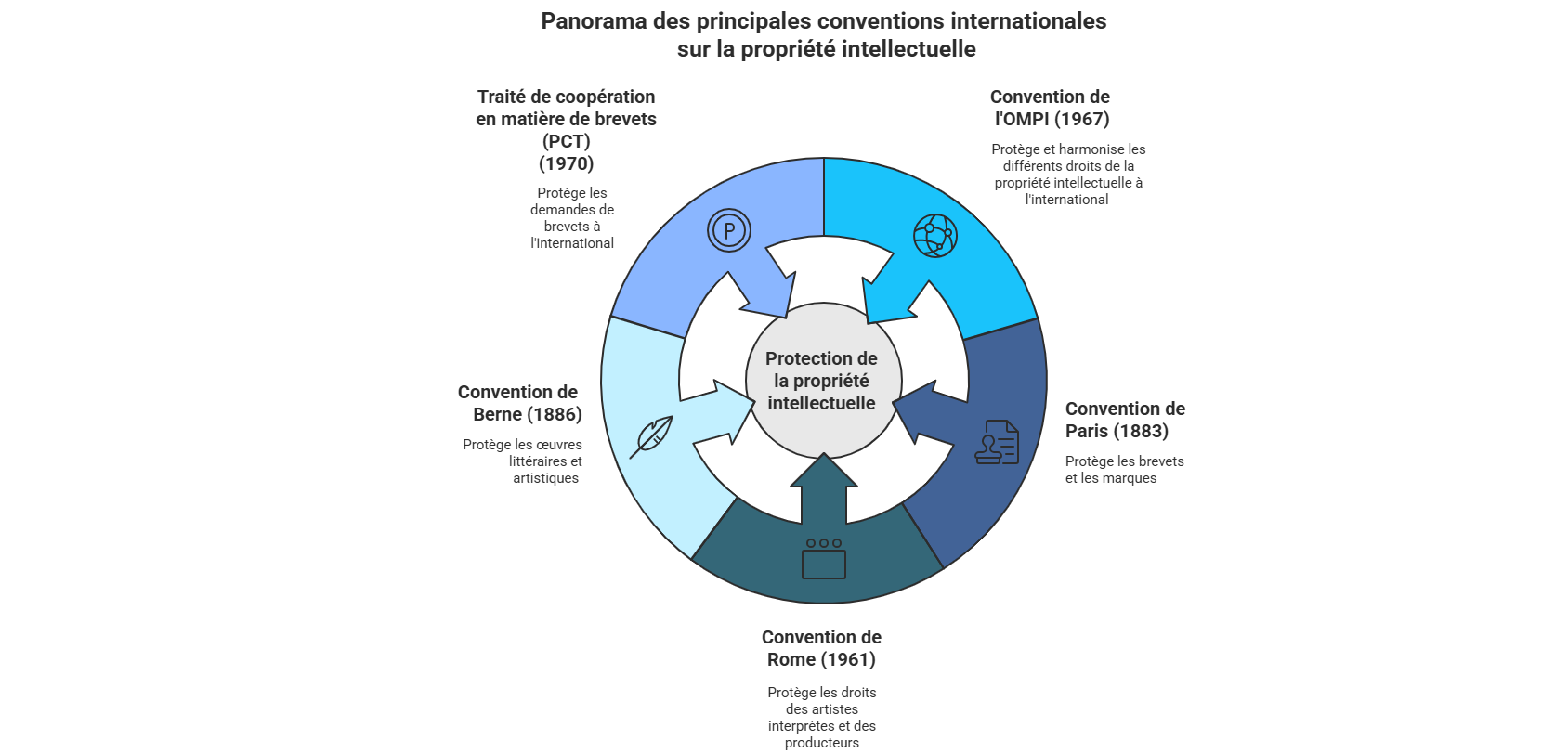
Le droit international de la propriété intellectuelle le plus largement reconnu est la Convention de l’Organisation Mondiale de la Propriété Intellectuelle (OMPI). Ce traité, signé par 169 pays en 1967 et mis à jour en 1996, définit les droits des inventeurs, des auteurs et des autres créateurs d’œuvres intellectuelles. L’OMPI est l’organisme international qui administre la Convention, qui énonce les principes et règles fondamentaux du droit international de la propriété intellectuelle. Elle fournit également un cadre pour la coopération internationale en matière de propriété intellectuelle et visent à harmoniser les différents droits nationaux de la propriété intellectuelle.
La Convention de l’OMPI est complétée par d’autres traités, tels que la Convention de Paris pour la protection de la propriété industrielle (1883), la Convention de Berne pour la protection des œuvres littéraires et artistiques (1886) et la Convention de Rome sur la protection des artistes interprètes ou exécutants, des producteurs de phonogrammes et des organismes de radiodiffusion (1961). Ces traités visent à protéger les droits de propriété intellectuelle sur différents types d’œuvres, telles que les œuvres artistiques, les dessins et modèles et les enregistrements sonores.
En savoir plus sur la convention de Paris ou sur le site de l’OMPI.
Un instrument clé pour la protection des brevets est également le Traité de coopération en matière de brevets (PCT) (1970). Administré par l’OMPI, le PCT permet à un inventeur, au moyen d’un dépôt unique, de protéger un brevet dans plusieurs pays à la fois, simplifiant ainsi considérablement les procédures et réduisant les coûts.
L’Accord ADPIC et la propriété intellectuelle liée au commerce
L’Accord sur les aspects des droits de propriété intellectuelle qui touchent au commerce (ADPIC) est un autre instrument juridique international important en matière de propriété intellectuelle. Élaboré par l’Organisation mondiale du commerce (OMC), cet accord définit les normes minimales de protection de la propriété intellectuelle que doivent respecter les pays membres de l’OMC. Il impose aux pays d’assurer certains niveaux de protection pour les brevets, les droits d’auteur, les marques et autres formes de propriété intellectuelle.
La dimension régionale et nationale
Outre ces conventions internationales sur la propriété intellectuelle, il existe également des accords régionaux qui protègent les droits de propriété intellectuelle. L’Union européenne, par exemple, dispose de son propre corpus législatif protégeant les droits de propriété intellectuelle. La directive de l’Union européenne relative aux droits de propriété intellectuelle (Directive 2004/48/CE du Parlement européen et du Conseil du 29 avril 2004) vise à harmoniser les règles régissant la protection de la propriété intellectuelle au sein de l’UE.
Conclusion
En résumé, un ensemble de normes internationales, régionales et nationales encadre la protection des droits des auteurs, inventeurs et autres créateurs d’œuvres intellectuelles. Ces dispositifs juridiques ont pour objectif de garantir la reconnaissance effective de leurs droits et d’assurer une rémunération équitable en contrepartie de leurs créations.
Le cabinet Dreyfus et Associés est en partenariat avec un réseau mondial d’avocats spécialisés en Propriété Intellectuelle et Nathalie Dreyfus avec l’aide de toute l’équipe du cabinet Dreyfus
FAQ
1. Qu’est-ce que l’OMPI et quel est son rôle ?
L’OMPI (Organisation Mondiale de la Propriété Intellectuelle) est une agence des Nations Unies chargée de promouvoir la protection de la propriété intellectuelle dans le monde. Elle administre plusieurs traités internationaux, dont la Convention de Paris et la Convention de Berne.
2.Quelle est la différence entre la Convention de Berne (1886) et la Convention de Paris (1883) ?
La Convention de Berne protège les œuvres littéraires et artistiques (droits d’auteur), tandis que la Convention de Paris protège les brevets et les marques.
3.Les règles de propriété intellectuelle sont-elles harmonisées à l’échelle mondiale ?
Pas exactement. Il existe des traités internationaux pour harmoniser les règles, mais chaque pays a sa propre législation nationale. L’Accord ADPIC impose des standards minimaux aux pays membres de l’OMC (Organisation Mondiale du Commerce).
4.Où trouver les différents textes de lois et traités internationaux en matière de propriété intellectuelle ?
Les textes officiels sont disponibles sur le site de l’OMPI.
Pour l’ADPIC, l’Accord est disponible sur le site de l’Organisation Mondiale du Commerce.