Legal definition, recent case law, litigation procedures, evidence methods and protection strategies — everything you need to know to protect your confidential information.
In an economy built on intangibles, a company’s value often lies in what it doesn’t disclose. Customer databases, algorithms, business strategies or technical know-how: these critical assets are not always patentable, and this is where trade secret protection comes into play.
Since the French law of July 30, 2018, transposing EU Directive 2016/943, France has had a powerful but demanding protective framework. The 2024-2025 case law has significantly clarified the relationship between trade secrets, the right to evidence and GDPR. This reference guide provides everything you need to understand, protect and defend your confidential information.
This guide covers:
- The legal definition and 3 cumulative protection criteria
- The 2024-2025 case law review and its practical implications
- Litigation procedures: taking legal action, timelines, costs
- Methods for proving the prior existence of your secret
- Industry case studies (pharma, tech, food & beverage)
- Coordination with other intellectual property rights
- The international dimension of protection
Evolution of the Legal Framework
| June 8, 2016 |
Adoption of EU Directive 2016/943 on trade secret protection |
| July 30, 2018 |
Transposition into French law (Law No. 2018-670) |
| December 22, 2023 |
Cass.Ass: admission of unfairly obtained evidence under conditions (No. 20-20.648) |
| June 5, 2024 |
Cass. Com.: first articulation between right to evidence / trade secrets (No. 23-10.954) |
| February 5, 2025 |
Cass. Com.: confirmation of the “indispensable” requirement (No. 23-10.953) |
| February 27, 2025 |
CJEU: GDPR prevails over trade secrets for automated decisions (C-203/22) |
1. Fundamentals: What is a Trade Secret?
Unlike traditional intellectual property (patents, trademarks) which relies on a public title, trade secret law protects information by virtue of it remaining secret. This protection arose from a simple observation: some strategic information cannot or should not be patented.
The Legal Definition (Article L.151-1 of the French Commercial Code)
To be protected by law, information must cumulatively meet three strict criteria:
The 3 Cumulative Conditions
- Secrecy
The information is not generally known or readily accessible to persons within circles that normally deal with this type of information. This is the “non-obviousness” criterion: the information must not be commonplace in the relevant sector.
- Commercial Value
The information has commercial value (actual or potential) precisely because it is secret. This value can be direct (competitive advantage) or indirect (cost avoidance).
- Reasonable Protection Measures
The information is subject to concrete protection measures by its holder to maintain its secrecy. This is often the determining criterion in litigation.
Essential Point
If you don’t actively protect your information (confidentiality clauses, passwords, document classification), courts will consider there is no trade secret. This is the criterion most often neglected by companies.
What Does Trade Secret Law Cover?
The scope is very broad. The concept of “information” is interpreted extensively and includes:
Technical know-how: manufacturing processes, recipes, chemical formulas, production methods, optimization parameters, technical drawings.
Commercial information: customer and prospect lists, pricing policies, supplier terms, product margins, internal market shares.
Strategic data: M&A projects, development plans, proprietary market studies, business plans, financial projections.
Organizational information: strategic organization charts, management methods, optimized internal processes.
Algorithms and data: source code, scoring models, proprietary databases, software architectures.
What Trade Secret Law Does NOT Protect
Understanding the limits of this protection is essential:
Independent discovery: if a competitor independently develops the same information, you cannot sue them.
Lawful reverse engineering: analyzing a product placed on the market to understand how it works is legal (unless contractually prohibited).
Information becoming public: once a secret is disclosed (voluntarily or not), protection is lost definitively.
General employee skills: the know-how acquired by an employee (their “experience”) belongs to them and can be used with a new employer.
2. 2024-2025 Case Law Review
Recent judicial developments have been marked by an ongoing tension between two imperatives: protecting business secrets and the right to evidence (a party’s need to obtain documents to assert their rights in court).
The Landmark Ruling: Cass. Com., February 5, 2025 (No. 23-10.953)
This was the major turning point. In a case between the franchise networks Speed Rabbit Pizza and Domino’s Pizza, the French Cour de Cassation established a structuring principle for balancing these rights.
The Legal Principle
“The right to evidence may justify the production of elements covered by trade secrets, provided that such production is indispensable to its exercise and that the infringement is strictly proportionate to the aim pursued.”
Practical implications:
For a judge to order production of a document covered by trade secrets, it must be indispensable to resolve the dispute, not merely “necessary” or “useful”. The term “indispensable” is intentionally restrictive: it excludes “fishing expedition” requests (exploratory evidence gathering).
The judge must conduct a proportionality assessment between the competing rights. This involves verifying that no less intrusive means of proof exists, and that the requested document is truly decisive for the outcome of the case.
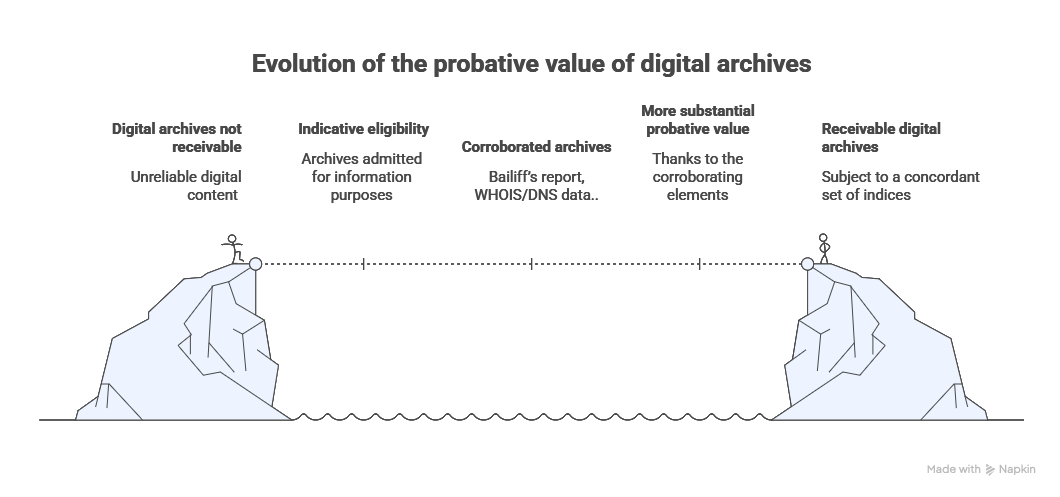
Managing Seizures (Seizure-Infringement and Article 145 CPC)
When a company is subject to an ex parte seizure on its premises, how can it prevent its secrets from ending up with a competitor?
Case law requires strict application of provisional sequestration:
Documents seized that may violate trade secrets are placed in escrow with a third party (usually the bailiff). A period of one month is granted to the seized party to contest disclosure. The judge rules on whether documents can be communicated before any transmission to the seizing party, applying the proportionality test.
The Preparatory Ruling: Cass. Com., June 5, 2024 (No. 23-10.954)
This decision laid the groundwork for the balance, recognizing for the first time that the right to evidence could justify an infringement of trade secrets, while requiring strict judicial oversight.
Unfairly Obtained Evidence: Cass.Ass, December 22, 2023 (No. 20-20.648)
The French Cour de cassation ruled that evidence obtained unfairly (secret recordings, stolen documents) may be admitted in court if two conditions are met: production is indispensable to exercising the right to evidence, and the infringement of the opposing party’s rights is proportionate to the aim pursued.
3. Trade Secrets vs GDPR: The CJEU Ruling of February 27, 2025
At the European level, the Court of Justice (CJEU, C-203/22, Dun & Bradstreet Austria) issued a major decision on the relationship between trade secrets and individual rights.
The Facts
An Austrian consumer was denied a mobile phone contract on the grounds of insufficient creditworthiness. This refusal was based on an automated assessment (credit scoring) conducted by Dun & Bradstreet. She requested an explanation of the “underlying logic” of this decision, invoking Article 15 of the GDPR (right of access). The company refused, citing trade secret protection of its algorithm.
The CJEU Decision
Principle Established by the CJEU
GDPR prevails over trade secrets regarding the right of access to personal data and information about automated decisions. The data controller must provide “meaningful information about the logic involved” in a manner that is “concise, transparent, intelligible and easily accessible”.
What this means for businesses:
Simply providing an algorithm or complex mathematical formula is not sufficient to fulfill the information obligation. The explanation must be understandable to a non-specialist.
The company must enable the individual to understand what data was used and how it influenced the decision. This doesn’t mean disclosing the complete algorithm, but explaining the determining criteria.
In case of dispute, allegedly protected information must be communicated to the judge who will balance the competing rights.
Sector Impact
This decision directly affects sectors using automated scoring: banks and credit institutions, insurance (personalized pricing), recruitment (automated CV screening), real estate rental (tenant creditworthiness), and more generally any automated decision-making process with significant effects on individuals.
4. Protection Strategies: “Reasonable Measures”
To benefit from legal protection, a company must prove it has implemented concrete measures. The term “reasonable” means appropriate to the nature of the information, the size of the company and the economic context. A SME doesn’t have the same resources as a Fortune 500 company, and courts take this into account.
Protection Measures Checklist
Legal Measures
- ☐ Non-disclosure agreements (NDAs): systematic before any discussion with a partner, service provider or investor
- ☐ Enhanced confidentiality clauses: in employment contracts and commercial agreements
- ☐ Non-compete clauses: for strategic positions, within legal limits
- ☐ IT charter: explicitly mentioning confidentiality duties and signed by all employees
- ☐ Internal regulations: incorporating confidentiality obligations
Technical Measures
- ☐ Access management: “need-to-know” principle
- ☐ Traceability: access logs for sensitive documents
- ☐ Encryption: of sensitive data at rest and in transit
- ☐ Strong authentication: MFA for access to critical systems
- ☐ DLP (Data Loss Prevention): data leak prevention tools
Organizational Measures
- ☐ Document marking: “CONFIDENTIAL — TRADE SECRET” label on sensitive documents
- ☐ Information classification: confidentiality level system (C1, C2, C3…)
- ☐ Staff training: awareness of social engineering risks and information leaks
- ☐ Exit procedures: reminder interview about obligations, retrieval of access and documents
- ☐ Physical security: secured premises for sensitive paper documents
- ☐ Secret inventory: regular mapping of the company’s confidential information
Practical Tip
“CONFIDENTIAL” marking of documents is the simplest and most effective measure to prove in court. An unmarked document will be difficult to consider as a trade secret. Also invest in traceability: being able to demonstrate who accessed what information and when is invaluable in litigation.
5. Proving Your Secret: Timestamping Methods
In case of dispute, you will need to prove that you held the information before the alleged infringement. A computer file’s creation date is not sufficient proof (it can be modified). You need to establish a certain date.
The Soleau Envelope (INPI)
The best-known and most economical solution for SMEs and individual inventors.
Principle: You send a document in two identical copies to INPI (French Patent Office). One copy is kept by INPI, the other is returned to you with an official stamp certifying the date.
Cost: €15 for 5-year protection, renewable once (10 years maximum).
Advantages: Simplicity, low cost, established judicial recognition.
Limitations: Limited size (7 pages maximum per compartment), not suitable for frequent updates, no direct international validity.
Website: INPI – Soleau Envelope
Deposit with a Bailiff or Notary
Traditional solution offering maximum evidentiary weight under French law.
Principle: A ministerial officer certifies the content of a document on a given date and stores it.
Cost: Variable depending on volume, generally €100 to €500 for a simple deposit.
Advantages: Uncontestable evidentiary weight, universal acceptance by French courts, ability to deposit digital media.
Limitations: Higher cost, less agile procedure for frequent updates.
Blockchain Timestamping
Modern solution, particularly suited for tech companies and frequent updates.
Principle: A digital fingerprint (hash) of your document is recorded in a public blockchain (usually Bitcoin or Ethereum). This record is immutable and timestamped.
Cost: A few euros per timestamp via specialized services, or integratable into your internal processes.
Advantages: Automatable, suitable for software development pipelines (CI/CD), low marginal cost, traceability of each version.
Limitations: Judicial recognition still emerging in France (but growing), need to keep the original document corresponding to the hash.
Providers: Woleet, OriginStamp, KeeSign, or solutions integrated into document management platforms.
APP Deposit (Software)
For source code and software, the French Agency for Program Protection offers a specialized deposit service.
Principle: Secure deposit of source code with certain date, recognized as proof of prior possession.
Cost: From €120 excluding VAT for 5 years.
Website: APP – Agency for Program Protection
Evidence Methods Comparison Table
| Method |
Cost |
Evidentiary Weight |
Ideal for |
| Soleau Envelope |
€15 / 5 years |
★★★★☆ |
SMEs, inventors, stable documents |
| Bailiff / Notary |
€100-500 |
★★★★★ |
Strategic deposits, foreseeable disputes |
| Blockchain |
€1-10 / hash |
★★★☆☆ |
Tech, source code, multiple versions |
| APP Deposit |
€120 / 5 years |
★★★★☆ |
Software, source code |
6. Taking Legal Action: Procedures, Timelines and Costs
When a trade secret infringement is identified, several courses of action are available to the secret holder. The choice depends on urgency, severity of the infringement and objectives pursued.
Competent Jurisdiction
Civil Court (Tribunal judiciaire): competent for civil actions in trade secret matters. This is the general jurisdiction court.
Commercial Court (Tribunal de commerce): competent if the dispute is between two merchants or commercial companies and relates to commercial acts.
Labor Court (Conseil de prud’hommes): competent if the infringement is committed by an employee within the employment relationship (but action may be brought before the civil court for non-employment aspects).
Available Procedures
Interim Relief (Référé)
Fast-track procedure for obtaining provisional measures. Conditions: urgency and absence of serious dispute, or existence of imminent harm. Hearing timeline: generally 2 to 4 weeks after service. The judge can order provisional prohibition on use or disclosure of the secret, protective seizure of disputed products or documents, and penalty payments to ensure compliance.
Proceedings on the Merits
Full procedure for obtaining a definitive decision. Average duration: 12 to 24 months at first instance depending on complexity. Allows for final damages, permanent injunction and publication of the judgment.
Adapted Seizure-Infringement (Article L.152-3 of the Commercial Code)
Ex parte procedure (without the opposing party being notified) to establish an infringement and seize evidence. Application to the president of the civil court. Execution by bailiff at the presumed infringer’s premises. Sequestration of sensitive documents pending decision on their disclosure.
Limitation Period
Limitation Period: 5 Years
Civil action in trade secret matters is time-barred after 5 years from the day the trade secret holder knew or should have known the last fact enabling them to exercise their action (Article L.152-2 of the Commercial Code). This period can be interrupted by a formal notice or legal proceedings.
Cost Estimates
| Procedure |
Attorney Fees (estimate) |
Ancillary Costs |
| Formal Notice |
€500 – €1,500 |
— |
| Simple Interim Relief |
€3,000 – €8,000 |
Bailiff: €200-500 |
| Seizure-Infringement |
€5,000 – €15,000 |
Bailiff: €1,000-3,000 |
| Proceedings on Merits (1st instance) |
€10,000 – €50,000+ |
Court expert: variable |
These estimates are indicative and vary according to case complexity, firm reputation and geographic area.
Elements to Gather Before Taking Action
Before initiating proceedings, ensure you have the following elements:
Proof of prior possession: Soleau envelope, notarial deposit, blockchain timestamp.
Proof of protection measures: signed NDAs, IT charters, access logs, document classification.
Proof of infringement: disclosed documents, infringing products, witness statements, correspondence.
Damage assessment: loss of revenue, lost R&D investments, reputational harm.
7. Remedies and Sanctions
In case of theft, misappropriation or unlawful disclosure, the law provides for extensive civil sanctions. Criminal liability remains limited to related offenses such as theft, breach of trust or receiving stolen goods.
What the Court Can Order
Prohibition orders: prohibition on using, manufacturing, marketing or disclosing the protected information. This prohibition may be accompanied by penalty payments for non-compliance.
Recall and destruction measures: product recall from the market, destruction of documents, files or products incorporating the secret (“infringing goods”).
Publication of the decision: at the infringer’s expense, in newspapers or on websites, to repair reputational harm.
Damages: calculated taking into account negative economic consequences (loss of earnings, lost opportunity), moral damage, and profits made by the infringer through the infringement.
Legal Exceptions (Article L.151-8 of the Commercial Code)
Trade secrets cannot be invoked in certain situations of overriding interest:
Exercise of the right to information: freedom of expression and freedom of the press, particularly to reveal information in the public interest.
Whistleblowers: disclosure of illegal activity or wrongdoing to protect the public interest (enhanced protection under the 2022 Waserman law).
Protection of a legitimate interest: particularly the right to evidence, subject to proportionality conditions established by 2025 case law.
Employee representatives: in the exercise of their functions (works council, union delegates).
8. Industry Case Studies
Trade secret protection is implemented differently across industries. Here are concrete examples illustrating the stakes and best practices.
Pharmaceutical and Biotechnology Industry
Typical Case: Protection of Development Data
A laboratory develops a new molecule. Before filing a patent (which requires disclosure), all R&D data constitutes critical trade secrets: preclinical trial results, tested formulations, observed side effects, synthesis processes.
Issue: A leak could allow a competitor to file a “blocking” patent or develop a similar molecule.
Recommended specific measures:
Strict compartmentalization of R&D teams (each team only has access to their part of the project). Laboratory notebooks timestamped and signed daily. Enhanced NDAs with CROs (Contract Research Organizations). Clean room procedures for license negotiations.
Technology Sector (Startups, Software Publishers)
Typical Case: Protection of Algorithms and Source Code
A startup develops a recommendation algorithm that constitutes its competitive advantage. The source code and model training parameters are trade secrets.
Issue: A developer leaving for a competitor could recreate a similar solution.
Recommended specific measures:
Technical architecture limiting access to complete code (microservices, module-based access). Systematic blockchain timestamping of commits. Specific confidentiality clauses in developer employment contracts. Monitoring of code repositories (GitHub, GitLab) to detect leaks. Formalized exit interviews with reminder of obligations.
Food and Beverage Industry
Typical Case: Protection of Recipes and Processes
A food manufacturer holds a unique recipe (sauce, beverage, processed product) whose secrecy is key to its market positioning. The most famous example is Coca-Cola, whose formula has been kept secret since 1886.
Issue: Disclosure would allow immediate copying by competitors or private labels.
Recommended specific measures:
Fragmentation of the recipe (different people know different parts). Coding of ingredients (internal codes instead of actual names). Restricted physical access to sensitive production areas. Regular audits of key ingredient suppliers.
Consulting and Professional Services
Typical Case: Protection of Methodologies and Client Data
A consulting firm develops proprietary methodologies and holds strategic data about its clients. These elements constitute major intangible assets.
Issue: A consultant leaving for a competitor takes their “address book” and methods.
Recommended specific measures:
Formal documentation of methodologies marked “trade secret”. Strict policy on use of client data (no export, anonymization). Client non-solicitation clauses. Team training on the distinction between personal skills and company assets.
9. Coordination with Other IP Rights
Trade secrets are not intellectual property rights in the strict sense, but they interact with other available protections. An effective protection strategy often combines several regimes.
Trade Secrets and Copyright
Cumulation possible: Software source code can simultaneously benefit from copyright (which protects the original form of expression) and trade secret protection (which protects the underlying algorithms and business logic).
Key differences:
| Criterion |
Copyright |
Trade Secret |
| Formality |
None (automatic protection) |
Protection measures required |
| What is protected |
The original form |
The information itself |
| Duration |
70 years post mortem |
As long as secrecy is maintained |
Trade Secrets and Patents
Strategic choice: To patent or keep secret? This choice is fundamental and irreversible.
Patenting is preferable when: The invention is easily identifiable through reverse engineering. You want to monetize the invention (licenses, assignments). The commercial lifespan is less than 20 years. You need a title enforceable against all (including independent discoverers).
Secrecy is preferable when: The information doesn’t meet patentability criteria. The secret can be maintained long-term (no reverse engineering possible). The commercial lifespan exceeds 20 years. You want to avoid patent costs and disclosure.
Warning: Patents Destroy Secrecy
Filing a patent requires publication of the invention (18 months after filing). This disclosure is definitive: if the patent is invalidated or expires, the information remains in the public domain. The secret is lost forever.
Trade Secrets and Trademarks
Coordination: Trademarks protect a distinctive sign (public by nature), while trade secrets can protect brand strategy, positioning studies, launch projects before public announcement.
Trade Secrets and Designs
Coordination: Before launching a new design, plans and prototypes are trade secrets. Once the product is marketed, protection shifts to design rights (registered or unregistered for the EU).
Trade Secrets and Know-How in Contracts
In know-how license agreements or franchises, trade secrets are often the basis of the transferred value. Confidentiality clauses must be particularly carefully drafted, with a precise definition of the know-how scope, protection obligations for the licensee, and control mechanisms.
10. International Dimension
In a globalized economy, your trade secrets cross borders. Understanding the international protection framework is essential.
The Harmonized European Framework
EU Directive 2016/943 has harmonized protection across the 27 member states. This means the definition of trade secrets and available remedies are similar throughout the European Union, facilitating cross-border protection.
The TRIPS Agreement (WTO)
Article 39 of the Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) requires the 164 WTO members to protect “undisclosed information”. This is the minimum ground of international protection.
International Comparison
| Jurisdiction |
Protection Level |
Particularities |
| United States |
★★★★★ |
Defend Trade Secrets Act (DTSA, 2016). Federal action available. Punitive damages up to 2x. Ex parte seizures. |
| European Union |
★★★★☆ |
Harmonized Directive 2016/943. Civil protection. No harmonized criminal component. |
| United Kingdom |
★★★★☆ |
Common law + directive transposition (retained post-Brexit). Breach of confidence. |
| China |
★★★☆☆ |
Revised Anti-Unfair Competition Law (2019). Improved protection but variable enforcement. |
| Japan |
★★★★☆ |
Unfair Competition Prevention Act. Criminal provisions. Effective protection. |
Best Practices for International Protection
Adapt your NDAs to applicable law: An NDA governed by French law won’t have the same effectiveness before an American or Chinese court. Include choice of law and jurisdiction clauses.
Map your information flows: Identify where your secrets transit (subsidiaries, subcontractors, cloud). Each jurisdiction crossed requires a protection analysis.
Strengthen clauses with foreign partners: In some countries with weaker protection, stricter contractual clauses (penalties, bank guarantees) can compensate.
Consider international arbitration: For cross-border disputes, arbitration (ICC, LCIA) can offer faster proceedings and facilitated enforcement in many countries (New York Convention).
11. Patent vs Trade Secret: Comparison Table
| Criterion |
Patent |
Trade Secret |
| Nature |
Public industrial property title |
Protection through confidentiality |
| Duration |
20 years maximum (with annuity payments) |
Unlimited as long as secrecy is maintained |
| Condition |
Public disclosure required |
Maintenance of secrecy required |
| Protection against |
All exploitation, including independent creation |
Unlawful acquisition only (not lawful reverse engineering) |
| Initial cost |
High (drafting, filing, examination: €5,000-15,000) |
Low (internal organizational measures) |
| Recurring cost |
Increasing annuities + international extensions |
Security measure maintenance |
| Main risk |
Design-around by different conception |
Leak or independent discovery |
| Monetization |
Easily monetizable (license, assignment, collateral) |
More complex monetization (due diligence required) |
| Ideal for |
Patentable technical inventions, monetization/licensing |
Know-how, commercial data, non-patentable information |
Combined Strategy
The two protections are not mutually exclusive. An optimal strategy can combine: patenting key innovations (strong, monetizable protection) and keeping complementary information secret (manufacturing processes, optimization parameters, implementation know-how).
12. Q&A: Your Questions About Trade Secrets
What is the difference between a patent and a trade secret?
A patent grants a 20-year monopoly in exchange for public disclosure of the invention. A trade secret protects information as long as it remains secret (unlimited duration), but does not protect against independent discovery by a competitor (lawful reverse engineering). A patent is enforceable against everyone; a trade secret only protects against unlawful acquisition.
Can an employee use their knowledge with a new employer?
Yes, acquired know-how (“experience”) belongs to the employee. The line is crossed if they take documents, client files or use specific technical secrets identified as confidential by their former employer. The distinction lies in the nature of the information: general skills (usable) vs. protected information (prohibited).
What constitutes a “reasonable protection measure”?
There is no official list, but case law recognizes: “Confidential” marking of documents, restricted computer access, signed confidentiality clauses, physical security of premises and staff training. Complete absence of such measures prevents legal protection. “Reasonable” is assessed according to company size and nature of the information.
Do trade secrets override whistleblower protections?
No. The law provides clear exceptions (Article L.151-8 of the Commercial Code). Trade secrets cannot be invoked to prevent disclosure of illegal activity or wrongdoing aimed at protecting the public interest (right to alert). The 2022 Waserman law strengthened this protection.
How long does protection last?
It is potentially perpetual. It lasts as long as the three conditions (secrecy, value, protection) are met. If the information becomes public — through disclosure, leak or independent discovery — protection is immediately and definitively lost. The example of Coca-Cola’s formula (kept secret since 1886) illustrates this potentially unlimited duration.
Can trade secrets yield to the right to evidence?
Yes, since the French Cour de cassation’s ruling of February 5, 2025 (No. 23-10.953). The judge must verify whether production of the document is “indispensable” to prove the alleged facts and whether the infringement of secrecy is “strictly proportionate” to the aim pursued. This is a case-by-case assessment that excludes exploratory requests.
Must I explain my algorithms to affected individuals?
Since the CJEU ruling of February 27, 2025 (C-203/22), yes for automated decisions with significant effects (scoring, profiling). You must provide “meaningful information about the logic involved” in an understandable manner. This doesn’t mean disclosing the complete algorithm, but explaining the criteria used and their influence on the decision.
What is the limitation period for legal action?
Civil action is time-barred after 5 years from the day the trade secret holder knew or should have known the last fact enabling them to exercise their action (Article L.152-2 of the Commercial Code). This period can be interrupted by a formal notice or legal proceedings.
How can I prove I held the information before the infringement?
Several methods establish a certain date: the Soleau envelope (INPI, €15 for 5 years), deposit with a bailiff or notary, blockchain timestamping, or APP deposit for software. A computer file’s creation date is not sufficient proof as it can be modified.
Can source code be protected by both copyright and trade secrets?
Yes, these two protections can be combined. Copyright protects the original form of the code (automatically, without formalities), while trade secret law protects the underlying algorithms and business logic (provided the 3 legal criteria are met and confidentiality is maintained).
Legal References
Need to Audit Your Protection or Take Legal Action?
Dreyfus assists you in implementing your protection measures, drafting your NDAs, timestamping your secrets and defending your interests in case of infringement.
Contact Our Experts




















 *Image generated by DALL E 3 Microsoft Version
*Image generated by DALL E 3 Microsoft Version


 The history of Birkenstock dates back to 1774 when Johann Adam Birkenstock opened his first shoemaker’s shop in Frankfurt. In 1897, the Birkenstock company was founded with the aim of creating comfortable shoes for workers and people with foot problems. The brand’s popularity grew in Germany and expanded internationally in the 1960s. Today, Birkenstock is synonymous with comfort and foot wellness. The Birkenstock sandal has become an icon of fashion and comfort, thanks to its cork and latex footbed that is moulded to the contours of the foot.
The history of Birkenstock dates back to 1774 when Johann Adam Birkenstock opened his first shoemaker’s shop in Frankfurt. In 1897, the Birkenstock company was founded with the aim of creating comfortable shoes for workers and people with foot problems. The brand’s popularity grew in Germany and expanded internationally in the 1960s. Today, Birkenstock is synonymous with comfort and foot wellness. The Birkenstock sandal has become an icon of fashion and comfort, thanks to its cork and latex footbed that is moulded to the contours of the foot.


 EUIPO, R 275/2023-4, September 13, 2023, TVAR VIRTUÁLNÍ STŘELNÉ ZBRANĚ (fig.)
EUIPO, R 275/2023-4, September 13, 2023, TVAR VIRTUÁLNÍ STŘELNÉ ZBRANĚ (fig.)
 Introduction
Introduction

 Generative artificial intelligence (AI) is a type of artificial intelligence system that can generate text, images, and other media.
Generative artificial intelligence (AI) is a type of artificial intelligence system that can generate text, images, and other media.






 Intellectual property (IP) is a valuable asset that can help businesses grow and protect their investments. Without adequate IP protection, businesses are vulnerable to having their ideas and inventions stolen or copied without any legal recourse. This article will discuss the pitfalls of not having IP protection in place and the importance of having it.
Intellectual property (IP) is a valuable asset that can help businesses grow and protect their investments. Without adequate IP protection, businesses are vulnerable to having their ideas and inventions stolen or copied without any legal recourse. This article will discuss the pitfalls of not having IP protection in place and the importance of having it.
 The advent of
The advent of 
 As an
As an
 Intellectual property (IP) litigation is a process used to resolve a dispute over the ownership or use of IP. It is a legal process that can be used to protect and enforce the rights of IP owners. IP litigation is an important tool for businesses, as it enables them to protect their valuable IP assets and to prevent infringement.
Intellectual property (IP) litigation is a process used to resolve a dispute over the ownership or use of IP. It is a legal process that can be used to protect and enforce the rights of IP owners. IP litigation is an important tool for businesses, as it enables them to protect their valuable IP assets and to prevent infringement.


 Contract law is an area of law that governs the enforcement of contracts and the related legal implications. It is a complex and multifaceted field of law that is applicable in many different scenarios. The European Union (EU) has its own set of contract law regulations that are specifically tailored to the needs of the EU. It is important for businesses, lawyers, and individuals to understand the basics of contract law in the EU in order to effectively navigate the legal landscape.
Contract law is an area of law that governs the enforcement of contracts and the related legal implications. It is a complex and multifaceted field of law that is applicable in many different scenarios. The European Union (EU) has its own set of contract law regulations that are specifically tailored to the needs of the EU. It is important for businesses, lawyers, and individuals to understand the basics of contract law in the EU in order to effectively navigate the legal landscape.
 In the digital age, there are a variety of ways in which businesses can be exposed to intellectual property (IP) litigation. As technology has become increasingly pervasive in our lives, the risk of litigation has increased along with it. The best way to protect your business from IP litigation is to take proactive steps to minimize the risk. Here are some tips for reducing the chances of being taken to court for an IP-related dispute.
In the digital age, there are a variety of ways in which businesses can be exposed to intellectual property (IP) litigation. As technology has become increasingly pervasive in our lives, the risk of litigation has increased along with it. The best way to protect your business from IP litigation is to take proactive steps to minimize the risk. Here are some tips for reducing the chances of being taken to court for an IP-related dispute.


 The world of technology is ever-evolving, and the same applies to the law that governs it. The latest development is Web 3.0 law, which is the legal framework created to govern the newest generation of technology and the internet. This article will explain what Web 3.0 law is and how it can affect businesses.
The world of technology is ever-evolving, and the same applies to the law that governs it. The latest development is Web 3.0 law, which is the legal framework created to govern the newest generation of technology and the internet. This article will explain what Web 3.0 law is and how it can affect businesses.
 Intellectual property (IP) is a valuable asset for businesses, and it is important for companies to understand the legal implications of IP contracts in the EU. Companies that operate in the EU should be aware of the various legal requirements that need to be considered when drafting an IP contract. This article will discuss some of the important considerations to be taken into account when drafting an IP contract in the EU.
Intellectual property (IP) is a valuable asset for businesses, and it is important for companies to understand the legal implications of IP contracts in the EU. Companies that operate in the EU should be aware of the various legal requirements that need to be considered when drafting an IP contract. This article will discuss some of the important considerations to be taken into account when drafting an IP contract in the EU.
 Technology is more integral to our lives and businesses than ever before. With this shift, the need for sound legal protection of technology-related assets has grown as well. This is where IT law comes into play. IT law, or information technology law, is a branch of law that covers the use, development, and implementation of technology. It’s a complex and ever-evolving area of law, and it can be the difference between success and failure for many businesses.
Technology is more integral to our lives and businesses than ever before. With this shift, the need for sound legal protection of technology-related assets has grown as well. This is where IT law comes into play. IT law, or information technology law, is a branch of law that covers the use, development, and implementation of technology. It’s a complex and ever-evolving area of law, and it can be the difference between success and failure for many businesses.
 Copyright is an important form of intellectual property protection that authors, artists, and other creators of works can register in the European Union (EU). The EU has a harmonised copyright system that applies to all of its member states, making it easier to protect your work across the entire EU. Here are the steps for registering a copyright in the EU.
Copyright is an important form of intellectual property protection that authors, artists, and other creators of works can register in the European Union (EU). The EU has a harmonised copyright system that applies to all of its member states, making it easier to protect your work across the entire EU. Here are the steps for registering a copyright in the EU.


 Intellectual property (IP) is an ever-evolving concept that is used to protect creations of the mind. It includes inventions, literary and artistic works, symbols, names, and images used in commerce. Protecting this intangible property is critical to ensuring that creators, inventors, and business owners get the recognition and financial reward that they deserve for their work. Intellectual property protection comes in several forms and can be used to protect different types of intellectual property.
Intellectual property (IP) is an ever-evolving concept that is used to protect creations of the mind. It includes inventions, literary and artistic works, symbols, names, and images used in commerce. Protecting this intangible property is critical to ensuring that creators, inventors, and business owners get the recognition and financial reward that they deserve for their work. Intellectual property protection comes in several forms and can be used to protect different types of intellectual property.




 Whether you are an entrepreneur, author, artist or inventor, it is important that you understand the steps to maximize your intellectual property protection. Here are some strategies you can use to do so.
Whether you are an entrepreneur, author, artist or inventor, it is important that you understand the steps to maximize your intellectual property protection. Here are some strategies you can use to do so.
 Whether you are an inventor, an artist, or a company, it’s likely that you hold intellectual property rights that may be subject to a licensing agreement. Granting a license on an intellectual property (IP) asset offers a variety of benefits, ranging from generating additional income to safeguarding innovative ideas of your company. Understanding the advantages associated with leveraging your IP rights through a license will enable you to grasp the optimal strategy to pursue.
Whether you are an inventor, an artist, or a company, it’s likely that you hold intellectual property rights that may be subject to a licensing agreement. Granting a license on an intellectual property (IP) asset offers a variety of benefits, ranging from generating additional income to safeguarding innovative ideas of your company. Understanding the advantages associated with leveraging your IP rights through a license will enable you to grasp the optimal strategy to pursue.
 As technology and innovation develop, intellectual property (IP) rights are becoming increasingly important in the European Union (EU). From the self-employed to large companies, everyone can benefit from a sound IP strategy.
As technology and innovation develop, intellectual property (IP) rights are becoming increasingly important in the European Union (EU). From the self-employed to large companies, everyone can benefit from a sound IP strategy.
 When it comes to intellectual property law, it is important to understand the differences between copyrights and patents. Both copyrights and patents protect creators and inventors from having their work stolen or copied, but they do so in different ways.
When it comes to intellectual property law, it is important to understand the differences between copyrights and patents. Both copyrights and patents protect creators and inventors from having their work stolen or copied, but they do so in different ways.





 When it comes to protecting your intellectual property, it is important to hire a law firm that specializes in this area. An intellectual property law firm can provide you with legal advice and representation tailored to your specific needs. Here are some of the benefits of consulting with an intellectual property law firm.
When it comes to protecting your intellectual property, it is important to hire a law firm that specializes in this area. An intellectual property law firm can provide you with legal advice and representation tailored to your specific needs. Here are some of the benefits of consulting with an intellectual property law firm.
 Intellectual and industrial property law firms specialize in protecting the intangible assets of companies and individuals. They offer services ranging from registration to enforcement of industrial rights such as patents, trademarks or designs, and artistic rights such as copyrights. They also can help in drafting contracts related to intellectual rights. By hiring an intellectual property law firm, you can better protect your intangible assets and avoid costly litigation.
Intellectual and industrial property law firms specialize in protecting the intangible assets of companies and individuals. They offer services ranging from registration to enforcement of industrial rights such as patents, trademarks or designs, and artistic rights such as copyrights. They also can help in drafting contracts related to intellectual rights. By hiring an intellectual property law firm, you can better protect your intangible assets and avoid costly litigation.
 If you’re in business, you’ll undoubtedly have heard of intellectual and industrial property rights. But do you know what these rights are and how they can help protect you and your business from legal issues and disputes?
If you’re in business, you’ll undoubtedly have heard of intellectual and industrial property rights. But do you know what these rights are and how they can help protect you and your business from legal issues and disputes?
 Trademark law covers a set of specific rules, with subtleties, that a specialist can help you to best understand your trademark issues.
Trademark law covers a set of specific rules, with subtleties, that a specialist can help you to best understand your trademark issues.
 If you are a victim of copyright infringement in the European Union (EU), hiring an intellectual property specialist can be an invaluable move. Intellectual property law is a complex and ever-changing field, and having the support of a skilled professional to help you navigate the complexities of the EU legal system is essential. Even if you have a basic understanding of copyright law, counsel can provide the expertise you need to protect your rights and interests.
If you are a victim of copyright infringement in the European Union (EU), hiring an intellectual property specialist can be an invaluable move. Intellectual property law is a complex and ever-changing field, and having the support of a skilled professional to help you navigate the complexities of the EU legal system is essential. Even if you have a basic understanding of copyright law, counsel can provide the expertise you need to protect your rights and interests.
 If you are considering legal actions related to intellectual property, it is important to understand the difference between a patent specialist and a specialist in trademarks, designs, etc., otherwise known as a soft IP specialist. Both work with individuals, companies and other entities to ensure and optimize the protection of their intellectual property rights. However, they specialize in different areas of IP law.
If you are considering legal actions related to intellectual property, it is important to understand the difference between a patent specialist and a specialist in trademarks, designs, etc., otherwise known as a soft IP specialist. Both work with individuals, companies and other entities to ensure and optimize the protection of their intellectual property rights. However, they specialize in different areas of IP law.


 Intellectual property law is an ever-evolving field that covers a wide range of legal matters related to copyrights, trademarks, patents, trade secrets, and other forms of creative works. In today’s digital age, understanding the nuances of intellectual property law has become increasingly important for businesses, entrepreneurs, and individuals.
Intellectual property law is an ever-evolving field that covers a wide range of legal matters related to copyrights, trademarks, patents, trade secrets, and other forms of creative works. In today’s digital age, understanding the nuances of intellectual property law has become increasingly important for businesses, entrepreneurs, and individuals.


 In the European Union (EU), intellectual property rights are regulated by two offices: the European Intellectual Property Office (EUIPO) located in Alicante and the European Patent Office (EPO) located in Munich. Therefore, as an ordinary person or legal professional who owns an intellectual property right, you will probably need to hire a lawyer specialized in intellectual property in order to best protect. However, does this lawyer have to be licensed in the EU to practice? This means that if you are a company or an individual who owns intellectual property rights, you may need to hire an intellectual property lawyer to protect you and your business. Then it is important to consider, does that lawyer have to be licensed in the EU?
In the European Union (EU), intellectual property rights are regulated by two offices: the European Intellectual Property Office (EUIPO) located in Alicante and the European Patent Office (EPO) located in Munich. Therefore, as an ordinary person or legal professional who owns an intellectual property right, you will probably need to hire a lawyer specialized in intellectual property in order to best protect. However, does this lawyer have to be licensed in the EU to practice? This means that if you are a company or an individual who owns intellectual property rights, you may need to hire an intellectual property lawyer to protect you and your business. Then it is important to consider, does that lawyer have to be licensed in the EU?
 An intellectual property lawyer or attorney specializes in the protection and enforcement of intellectual property rights. Intellectual property (IP) rights protect intangible objects, such as inventions, intellectual works or trademarks. Depending on the country, these rights are governed by federal, state and international laws.
An intellectual property lawyer or attorney specializes in the protection and enforcement of intellectual property rights. Intellectual property (IP) rights protect intangible objects, such as inventions, intellectual works or trademarks. Depending on the country, these rights are governed by federal, state and international laws.
 Intellectual property (IP) lawyers and attorneys provide a variety of services to help protect a company’s or individual’s creations and inventions from being copied or misused. IP lawyers and attorneys specialize in the legal protection of copyrights, trademarks, patents, and trade secrets. These four areas of IP law are the main focus of IP attorneys, but they can also provide other services related to IP rights, such as drafting licensing agreements, infringement actions and litigation strategy.
Intellectual property (IP) lawyers and attorneys provide a variety of services to help protect a company’s or individual’s creations and inventions from being copied or misused. IP lawyers and attorneys specialize in the legal protection of copyrights, trademarks, patents, and trade secrets. These four areas of IP law are the main focus of IP attorneys, but they can also provide other services related to IP rights, such as drafting licensing agreements, infringement actions and litigation strategy.
 An intellectual property attorney is a lawyer specialized in intellectual property law, who has a mission to support the protection of intellectual creations. Intellectual property law includes industrial property such as patents, trademarks and designs, as well as literary and artistic property. Intellectual property lawyers have a unique set of skills and knowledge related to filing, drafting contracts, as well as litigation related to intellectual property rights.
An intellectual property attorney is a lawyer specialized in intellectual property law, who has a mission to support the protection of intellectual creations. Intellectual property law includes industrial property such as patents, trademarks and designs, as well as literary and artistic property. Intellectual property lawyers have a unique set of skills and knowledge related to filing, drafting contracts, as well as litigation related to intellectual property rights.
 eSports viewers may reach 29.6 million per month by the end of 2022, beginning of 2023, according to
eSports viewers may reach 29.6 million per month by the end of 2022, beginning of 2023, according to 
 When changing Facebook to Meta, Mark Zuckerberg tried to justify Meta as the future. The metaverse is indeed a reality for millions of online players, a place to meet, interact, and create in this new world.
When changing Facebook to Meta, Mark Zuckerberg tried to justify Meta as the future. The metaverse is indeed a reality for millions of online players, a place to meet, interact, and create in this new world.




 *Image generated by DALL-E 3, Microsoft Version
*Image generated by DALL-E 3, Microsoft Version
 Registering your trademark allows you to protect it. For a French trademark, it must be registered with the INPI (National Institute of Industrial Property), but the protection can be extended to the European Union (EUIPO) and internationally (WIPO). When a trademark is registered on the national territory, in order to extend its protection, it is possible to register the trademark within the European Union and internationally. There is a right of priority which allows to file other trademark applications while benefiting from the filing date of the first application. The priority period is six months for trademarks.
Registering your trademark allows you to protect it. For a French trademark, it must be registered with the INPI (National Institute of Industrial Property), but the protection can be extended to the European Union (EUIPO) and internationally (WIPO). When a trademark is registered on the national territory, in order to extend its protection, it is possible to register the trademark within the European Union and internationally. There is a right of priority which allows to file other trademark applications while benefiting from the filing date of the first application. The priority period is six months for trademarks.
 The digital transition of small and medium-sized enterprises was the AFNIC’s 2020 target – a year marked by the health and economic crisis. This target was reflected in the 2020
The digital transition of small and medium-sized enterprises was the AFNIC’s 2020 target – a year marked by the health and economic crisis. This target was reflected in the 2020 








 To the delight of our taste buds, flavors and gourmet creations are part of our daily lives, but from a legal perspective, the situation is more delicate and the flavor more bitter. Indeed, there is a consensus on the need to protect culinary creations but intellectual property law currently offers only peripheral protection.
To the delight of our taste buds, flavors and gourmet creations are part of our daily lives, but from a legal perspective, the situation is more delicate and the flavor more bitter. Indeed, there is a consensus on the need to protect culinary creations but intellectual property law currently offers only peripheral protection.
 On April 30, Spain finalized the reform of its trademark law, started in late 2018. From that date, the
On April 30, Spain finalized the reform of its trademark law, started in late 2018. From that date, the 
 Nathalie Dreyfus has been admitted as panelist and arbitrator in the CIRA Panel (Canadian Internet Registration Authority).
Nathalie Dreyfus has been admitted as panelist and arbitrator in the CIRA Panel (Canadian Internet Registration Authority).
 According to the
According to the 












 On February 1, 2019, a new version of the
On February 1, 2019, a new version of the 



 The Czech Republic has recently amended its Trademark law in order to transpose
The Czech Republic has recently amended its Trademark law in order to transpose 










 This year Nathalie Dreyfus and Dreyfus law firm were yet again recognized as “Excellent” in the category “Best Intellectual Property Law Firm in France” for brands and designs in 2019.
This year Nathalie Dreyfus and Dreyfus law firm were yet again recognized as “Excellent” in the category “Best Intellectual Property Law Firm in France” for brands and designs in 2019.


 Trademark law has long recognized the principle of specialty, which signifies that the owner of a trademark has a monopoly on its sign only for the goods and services that the sign designates. However, application of this principle needs a further consideration in cases related to alcoholic beverages.
Trademark law has long recognized the principle of specialty, which signifies that the owner of a trademark has a monopoly on its sign only for the goods and services that the sign designates. However, application of this principle needs a further consideration in cases related to alcoholic beverages.
 The withdrawal of the United Kingdom from the European Union, either with or without ratification of an agreement, will have an impact on trademark law, domain names, and personal data alike. It is therefore necessary to understand the changes and get prepared.
The withdrawal of the United Kingdom from the European Union, either with or without ratification of an agreement, will have an impact on trademark law, domain names, and personal data alike. It is therefore necessary to understand the changes and get prepared.

 It was after a lengthy procedure that the French Supreme Court, the Cour of Cassation, in its judgment delivered
It was after a lengthy procedure that the French Supreme Court, the Cour of Cassation, in its judgment delivered 
 The famous Alsatian Choucroute (Sauerkraut) was finally recognized on July 3rd, 2018 as a Protected Geographical Indication (PGI) at the European level. It provides an opportunity to revisit the term “protected geographical indication” and the challenges it represents on the local and international level.
The famous Alsatian Choucroute (Sauerkraut) was finally recognized on July 3rd, 2018 as a Protected Geographical Indication (PGI) at the European level. It provides an opportunity to revisit the term “protected geographical indication” and the challenges it represents on the local and international level.
 Samoa’s membership confirms that the Madrid System and its protocol are major assets for the international protection of the trademarks, offering a convenient and economic solution for trademark owners around the world.
Samoa’s membership confirms that the Madrid System and its protocol are major assets for the international protection of the trademarks, offering a convenient and economic solution for trademark owners around the world.






 The last ICANN meeting of the year was held in
The last ICANN meeting of the year was held in 
 In a
In a 
















 In the
In the 










 The auction house Camard used the services of a photographer to produce photographs for the different auction catalogues. They subsequently observed that Artprice.com had digitised these catalogues and published them online in their database, without authorisation.
The auction house Camard used the services of a photographer to produce photographs for the different auction catalogues. They subsequently observed that Artprice.com had digitised these catalogues and published them online in their database, without authorisation.






 In tandem with ever stricter legislation, new technologies are increasingly requesting our personal data, often of a sensitive nature.
In tandem with ever stricter legislation, new technologies are increasingly requesting our personal data, often of a sensitive nature.




 The very essence of copyright is to confer on the author of an original work an exclusive, intangible property right enforceable against all. Pursuant to this exclusive right, no infringement of the work, of any nature whatsoever, can be carried out without the prior consent of the author. The right to the respect of the integrity of the work enshrined in article L.121-1 of the Intellectual Property Code imposes that a work that expresses the personality of the author cannot in theory be subject to a material alteration without the express agreement of the author. Through a judgment on 20 December 2017, the Supreme Court of Appeal has just established a limit to this exclusive right of the author: an alteration of a work of architecture that does not infringe the rights of the author can be carried out without their consent. An original architectural work can be protected in respect of copyright as any other literary or artistic work would be. However, and contrary to a purely aesthetic work, a work of architecture has a functional purpose which results from the fact that a building, in addition to being original, may constitute a place of residence, work or access to culture. In the case at hand, the architectural work intended to house the collections of the “Musée d’Arles antique” had been produced by an architect on behalf of a département, which, without the consent of the architect, proceeded to carry out extension works to the building in order to exhibit a Gallo-Roman trading ship.
The very essence of copyright is to confer on the author of an original work an exclusive, intangible property right enforceable against all. Pursuant to this exclusive right, no infringement of the work, of any nature whatsoever, can be carried out without the prior consent of the author. The right to the respect of the integrity of the work enshrined in article L.121-1 of the Intellectual Property Code imposes that a work that expresses the personality of the author cannot in theory be subject to a material alteration without the express agreement of the author. Through a judgment on 20 December 2017, the Supreme Court of Appeal has just established a limit to this exclusive right of the author: an alteration of a work of architecture that does not infringe the rights of the author can be carried out without their consent. An original architectural work can be protected in respect of copyright as any other literary or artistic work would be. However, and contrary to a purely aesthetic work, a work of architecture has a functional purpose which results from the fact that a building, in addition to being original, may constitute a place of residence, work or access to culture. In the case at hand, the architectural work intended to house the collections of the “Musée d’Arles antique” had been produced by an architect on behalf of a département, which, without the consent of the architect, proceeded to carry out extension works to the building in order to exhibit a Gallo-Roman trading ship.

















































































 Compliance of Zambian law with the Paris Convention, the TRIPS Agreement and the Harare Protocol.
Compliance of Zambian law with the Paris Convention, the TRIPS Agreement and the Harare Protocol.









































 Dreyfus recently held a seminar on trademarks and domain names in Iran as international brands look toward the country for opportunities. Nathalie Dreyfus reveals what was discussed, and how brands can benefit.
Dreyfus recently held a seminar on trademarks and domain names in Iran as international brands look toward the country for opportunities. Nathalie Dreyfus reveals what was discussed, and how brands can benefit.

















 Following the results of the referendum and the resignation of David Cameron, Theresa May has now been appointed Prime Minister and shall lead the Brexit. As laid out in our previous articles on the Brexit (Brexit: How to prepare oneself for the consequences?; The consequences of Brexit on trademarks and patents), implications on intellectual property law are to be expected, and in particular, on trademark and patent law. Such implications however, are not yet clear.
Following the results of the referendum and the resignation of David Cameron, Theresa May has now been appointed Prime Minister and shall lead the Brexit. As laid out in our previous articles on the Brexit (Brexit: How to prepare oneself for the consequences?; The consequences of Brexit on trademarks and patents), implications on intellectual property law are to be expected, and in particular, on trademark and patent law. Such implications however, are not yet clear.